Course Introduction to Programming
Programming Languages
In this lesson, we will learn about Programming Languages, understanding their concept and the importance they have in software development.
We will also explore the different degrees of abstraction present in languages, analyzing how each level influences the way of programming.
What is a programming language?
A programming language is a method of communicating with the computer, of "telling" it exactly what you want it to do. They are a set of rules, syntax, and semantics that allow developers to write instructions that the computer can interpret and execute.
By mastering a programming language, you can create programs, a "manual" that tells the computer what it should do at any given moment.
Some examples of programming languages and their main applications are:
- C: Operating systems, Drivers and firmware, embedded programming
- C++: Competitive Programming, games, performance
- C#: Windows, games (Unity), back-end
- Java: Android, corporate systems
- Python: AI, data science, automation
- Javascript: Front-end, back-end (Node.js)
- among others...
The programming language you will study in this course will be the C language 😃
But, why not use the computer's language to program? Well, the language the computer understands is machine code, which consists of sequences of zeros and ones (the binary code). Thus, if we were to program directly in machine code, it would be:
- Extremely difficult: It would be almost impossible to read, write, and debug (find and correct errors)
- Unintuitive and nothing like our language: We would need to memorize hundreds of bit sequences for each small instruction.
- Hardware-dependent: Machine code is specific to each type of processor, so a program written in machine code for one processor would not work on another. High-level programming languages, on the other hand, are more portable.
Therefore, programming languages emerged to facilitate this entire process 😉
Importance
Before the invention of programming languages, programming already existed, but the problem was that the programmer had to know all the details of the hardware they would be working with for the program to function. In other words, the time and difficulty to program in the past were much, much greater. Thus, the creation of programming languages allowed, among other things:
- Ease of learning: Programming languages use a syntax closer to human language, with words and logical structures, making the learning process more intuitive and accessible.
- Greater productivity: With simpler and more efficient tools, developers can create and modify programs in a much shorter time.
- Create more complex programs: By simplifying the foundation, programming languages paved the way for the creation of much more sophisticated and robust software, which would be practically impossible to develop directly in machine code.
- Higher degree of abstraction for the programmer: They create an "abstraction layer" between the programmer and the hardware, allowing the developer to think about the program's logic and not the machine's specifics.
What are Degrees of Abstraction?
In computing, abstraction is the act of hiding complex details and showing only what is necessary to solve a problem. When applied to programming languages, abstraction can be understood as the level of ease of learning and use, measured by the proximity or distance from the language the computer actually understands (machine code). In this sense, we can distinguish two types of abstraction:
- Low-level: are languages close to the hardware, such as Assembly and machine code itself. In them, the programmer needs to deal with technical details, like registers and memory addresses. They are harder to use, but offer greater control and high performance, being widely used in embedded systems and in the development of operating systems.
- High-level: are languages close to human language, such as Python, C++, and C. They hide much of the computer's complexity, allowing the programmer to focus on the problem's logic instead of the hardware details. They are easier to learn and write, being widely used in web applications, data science, and artificial intelligence.
For example, compare the two code snippets, respectively, in Assembly and Python:
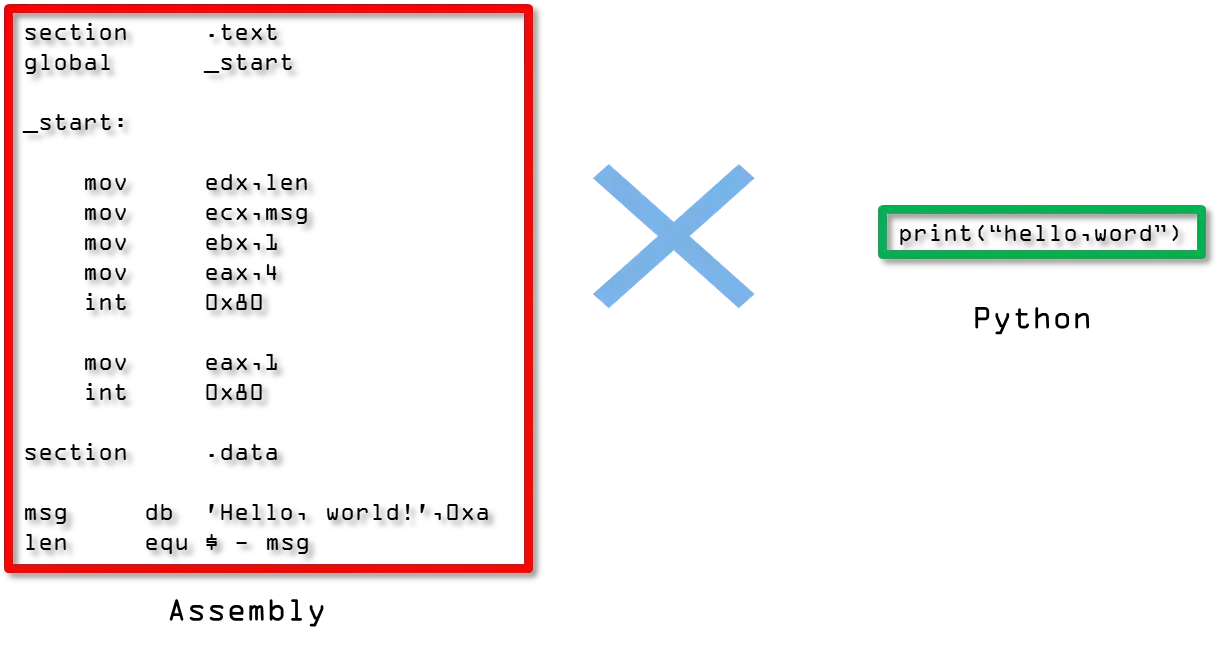
Figure 1 : Comparação entre Assembly e Python
As you can see, writing in Python is much more similar to the language we use daily.
You might be wondering: why would anyone still use machine language?
The idea is that the more a programming language resembles ours, the more the computer needs to “translate” what we write into the code it understands. Therefore, high-level languages are easier for us, but can be a bit slower for the computer to execute.
Conclusion
In this lesson, you learned what programming languages are, their importance, and how they facilitate communication with the computer. We saw the difference between low-level and high-level languages, understanding how the degree of abstraction influences learning, productivity, and the development of more complex programs.
Now you know the basic concepts of programming languages and why they are essential for creating software more easily, quickly, and efficiently 😃
